- Technical Guide
Industrial IoT Reference Book
Everything you need to know about Industrial IoT.
Table of Contents
Internet of Thing (IoT) is all about connecting the physical things and cyber (Internet) together to gather data / information about any things. Traditionally, centralizing the data data read from any given physical things was difficult due to lack of wireless interfaces. The advancement in sensor technologies and wireless communication enables to bridge this gap.
IoT is a concept of connecting various devices to the internet and among other connected devices. It is an ecosystem of connected physical devices/things that are made accessible through internet.
Any things or objects within an IoT system are assigned with a unique IP address. An IP address enables connectivity, activates data collection and data transfer over a network in the absence of manual intervention. In short, IoT is a huge network of a plethora of connected devices and gadgets that simultaneously collect and share data of the manners and environments in which it is being utilized.
Particularly, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the sub specification of IoT technology which is swiftly growing with remarkable innovations in connecting with industrial things. Industrial IoT technologies help to sense the data from physical things, process locally, communicate to cloud for storage through internet, aggregate data, analyze and produce actionable insights and intelligence out of it. Therefore, IIoT solutions are a combination of sensors, IoT gateway (a) edges, wireless communication (Cellular / LPWAN), cloud computing and data analytics etc.
Industrial IoT platform is a prebuilt software services help to manage the entire IoT technology landscape from sensor device management to intelligence and industry equipment automation from anywhere. Refer our Industrial IoT Platform comparison blog for more information.
Industrial IoT is the essential enabler of Industry 4.0, also known as Smart Industry. As a confluence of multiple technologies like wireless communication, M2M communication and AI for cognition that builds and strengthens a self-dependent industry by reducing manual operational errors.
In the business optimization interests of enterprises, adopting Industrial IoT based intelligence solutions facilitate to improve process efficiency and production optimization.
Example: When IoT connect, collect and analyze of real-time data of production, it is made it easier to see the real-time performance of the current production rather than later. Remote monitoring of industrial operations helps to plan the action ahead (such as equipment maintenance) in cost effective and reliably. IIoT helps to promote the innovation through open architectures that allow process customization and error-prone operations across a production equipment.
What is IoT Network?
IoT Network refers to the communication technologies used by Internet of Things (IoT) devices to share or spread the data to other device or interfaces available within reachable distance. There are various types of IoT networks available for IoT devices / IoT sensors to communicate. It is critical to choose proper networking protocol for given requirements in order to be able to collect data at real-time and access insights through IoT applications.
This technical reference book will explore various types of IoT networks available for IoT implementation and selection strategy.
As the industry revolutionizes with changing times, the current industry 4.0 is a recipient of advancement in telecom technology that has innovated the IoT (Internet of Things). The Industrial IoT (Industrial Internet of Things), a sub-specification of the IoT is designed to facilitate industry automation and enable Smart manufacturing. Industrial IoT focuses on parameters exclusive to the manufacturing industry and therefore exhibits potential growth, production, optimization and maintenance of industrial outputs and equipment, respectively. At the heart of IoT technology for industries, the choice of network plays a vital role in the success of Industrial IoT with Smart Manufacturing. Let’s explore wireless networks for smart manufacturing.
Layers of Network in IoT
In order to wisely choose which network appropriately supports the needs of an industry, it is advised to stay informed on network layers in the IoT space. IoT includes a lot of machine communication, device identification and communication, along with active machine learning tools for data analytics and therefore a robust network is required to support the same.
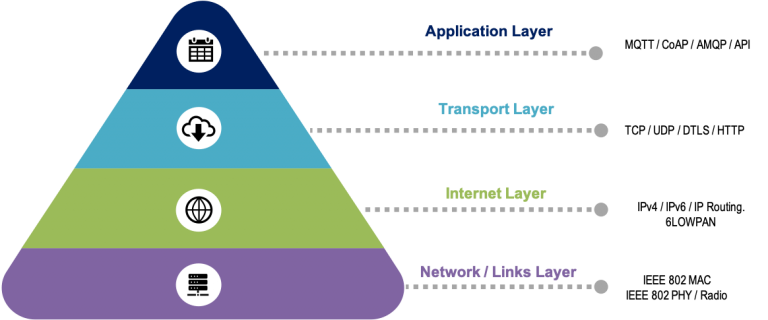
Owing to facilitate your understanding, here is a structure that pictures the network layering in IoT technology:
The first links layer is in line with the industry standards like that of IEEE 802 MAC and IEEE 802 PHY dealing with local and metropolitan area networks. It is restricted to short data transmission of uniformly sized cells. The next layer is the internet layer (IPv4/IPv6/IP Routing) that is internet-ready connected devices / systems that communicate within internet connected domains with the help of a device unique identification. Following the internet layer is the transport layer consisting of TCP/UDP/DTLS/HTTP over wire helps communicate between systems as part of transportation principles and protocols. At the apex is the application layer which accommodates industry standard approach like MQTT, CoAP, API for application communication between devices / systems.
Types of IoT Networks

From RFID scanning and communication to Bluetooth (BLE/NFC) data communication, progressive standards are being introduced for sophistication. Though BLE/NFC are mobile phone operation centric, there are other network protocols that serve the purpose of IoT deployment in line with industry pre-requisites. IoT deployment is supported by cellular (2G, 3G, 4G & 5G) network protocols along with WiFi / LoFI by providing efficient local area networking of short range among devices and internet access.
MESH protocols made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology connects devices and nodes for data transfer and communication that can be opted in IoT deployment based on the need of customers. The LPWAN (LoRa, sigfox) is a futuristic invention that refers to Low Power Wide Area Network that lowers power consumption while offering advanced network for connectivity. It is designed to facilitate long range wireless communications at a low bit rate among connected devices / systems.
Comparison of Wireless Network
Specific to wide area coverage, remote connectivity and maintenance that IoT deployment brings to industries with IIoT sub-specification, it is essential to compare and note the best wireless network based on IoT specifications to serve requirements of manufacturing industries. Wireless network can be accordingly customized.
IoT Network Spec | LTE-M / NB-IOT | LoRa | Sigfox | Cellular (3G/4G) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Specification | 3GPP | LoRa-Alliance (Open) | Sigfox (Private) | 3GPP |
Spectrum | Licensed | Unlicensed / Free | Unlicensed / Free | Licensed |
Bandwidth | 180 Mhz | 125 - 500 Khz | 200 Khz | 5Mhz - 20Mhz |
Data Rate | 200+ Kbps | 27 Kbps | 600 dB | 380+ Kbps |
Payload per day | Unlimited | Low | Low | High |
Power Consumption | Medium | Low | Low | High |
App Usage | Frequent Data | Frequent Data | Periodic Data | Streaming Data |
The above image indicates comparison of types of IoT networks specification between 4 large competitors across the globe for IoT deployments. Note that these are open specifications and it varies from providers to providers. The left side of the image indicates IoT network specification and the subsequent 4 columns indicate the wireless network providers. There are restrictions pertaining to the network service providers and what it offers, but it can be tailored to suit particular industry needs.
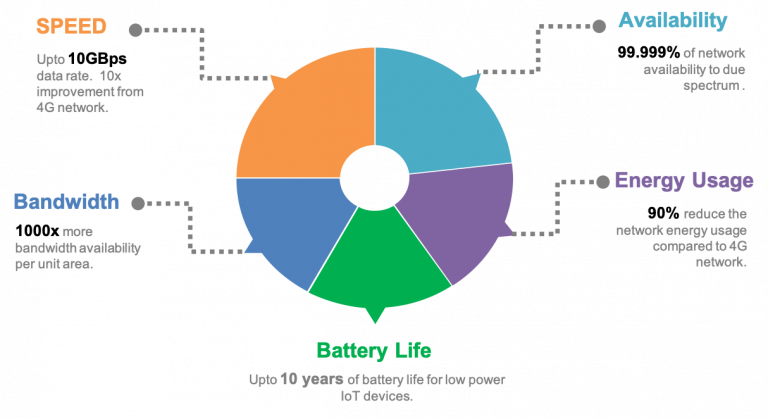
Since IoT deployments are usually remote, higher bandwidth, more speed for real-time data transmission is a mandatory requirement, fortunately 5G network is much advanced in these fields and therefore smoothens IoT deployment and functioning in manufacturing industries between remote units and production centers. Though currently 5G network is cellular based, owing to meet IoT standards with 5G network would require much more accessibility points across the globe. In the futuristic perspective, 5G wireless network broadens IoT prospects with its features to support smart industries, smart home and smart buildings.
IoT Network for Smart Manufacturing
Smart Manufacturing Use Cases | Data Rate | Network Required |
|---|---|---|
Predictive Maintenance | High Volume Data by Machines | Higher Data Rate / Unlimited |
Addictive Production | Bigger Size Data Feeding | Higher Volume |
Asset Performance Optimization | High Volume Data by Asset | Higher Volume |
Remote Services | Streaming Data to Command | Higher Data Rate / Unlimited |
Quality Control & Analysis | Moderate Data by Hour | Low Volume |
Inventory Optimization | Moderate Data by Hour | Low Volume |
Human Robot Collaboration | Streaming Data to Command | Higher Data Rate / Unlimited |
The above mentioned use case specifications are central to smart manufacturing. Example: Features like predictive maintenance that predicts machine work optimized duration and schedules down-time requires high volume of data transmission at real-time by machine condition monitoring to perform prediction. As a result, it demands higher data rate at unlimited service. Likewise, the image helps read and analysis similar use case specification, data volume and required network type.
Wireless Network Selection Strategy
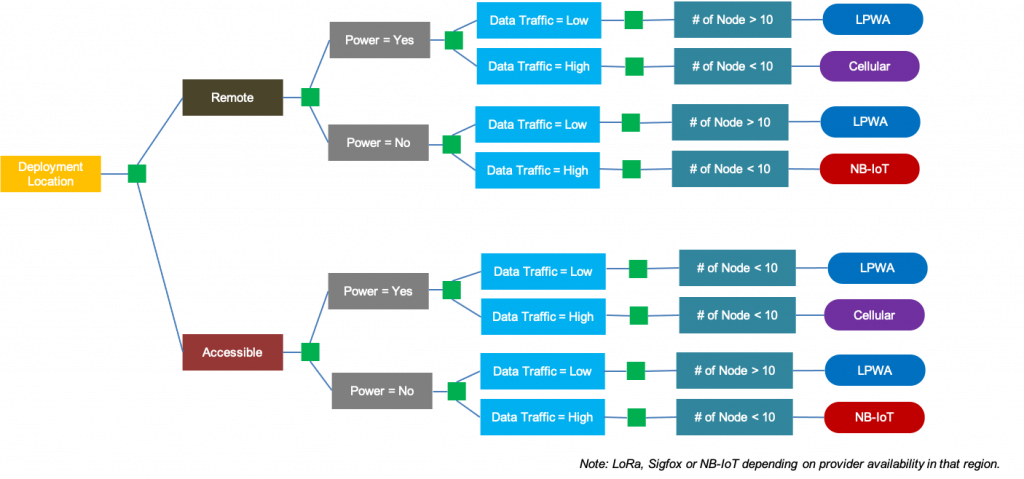
A similar ‘Decision Tree’ can be sketched, primarily keeping in mind, the deployment location. Once the location (remote, accessible) is noted, the availability of power supply is to be assessed. Following which, data traffic assessment can be made pertaining to volume of real-time data to be transferred. Depending on the data, number of required nodes can be established and the wireless network can be opted accordingly. Using the above image as a model, a customized ‘Decision Tree’ can be prepared.
As concluding notes, wireless network for successful Smart manufacturing with IoT is a necessity. Prior thoughtful decisions are to be taken for valuable results with IoT technology in the manufacturing industry. Use this guide to explore detailed precisions for wireless network connectivity to strong-arm your entire manufacturing industry (across borders) for unhindered efficient industry and production operations.