In the manufacturing industry, ensuring the reliability of machinery and equipment is essential for maintaining consistent production quality and minimizing costly downtime. Reliability management in manufacturing focuses on maximizing the performance, lifespan, and efficiency of assets through proactive maintenance, data analysis, and condition monitoring.
By adopting reliable management practices, manufacturers can reduce unexpected breakdowns, optimize operational costs, and improve overall productivity, all while extending the life of their critical assets. Emphasizing reliability management helps manufacturers stay competitive by ensuring that their equipment runs smoothly, efficiently, and cost-effectively.
What is Asset Reliability Management?
Asset Reliability Management (ARM) is a practice that systematically manages physical assets to maximize availability, dependability, performance, and overall efficiency. Asset reliability generally refers to the ability of a physical asset or piece of equipment to perform its intended function without failure or breakdown over a specified period.
Industrial organizations such as manufacturing, energy, transportation, and others heavily rely on different types of assets, such as machinery, equipment, and instruments, to achieve their operational objectives.
Reliability practice is a key aspect of asset maintenance management. The goal is to prevent unexpected operational failures and disruptions, which can lead to increased costs, safety hazards, and a negative impact on overall business performance.

Key Values of Asset Reliability Management (ARM)
Asset Reliability Management (ARM) brings several key values to organizations, ensuring that assets are well-maintained and continue to perform optimally. Here are the primary benefits of implementing ARM:
- Increased Uptime: One of the most significant values of ARM is minimizing unplanned downtime. By identifying potential issues before they result in failures, ARM helps to maintain a continuous production flow, avoiding costly disruptions to operations.
- Cost Savings: ARM reduces maintenance costs by preventing unnecessary repairs and optimizing maintenance schedules. Predictive maintenance strategies ensure that resources are used efficiently, and repairs are only made when necessary, leading to significant cost reductions.
- Extended Asset Lifespan: Proactively managing asset health through condition monitoring and timely maintenance helps extend the life of critical equipment. By preventing premature wear and tear, ARM ensures that assets reach their full operational potential.
- Improved Safety and Compliance: Well-maintained assets are less likely to fail and cause safety hazards. ARM enhances workplace safety by ensuring that machinery and equipment operate within safe parameters and meet regulatory compliance standards.
- Optimized Performance: ARM improves the overall performance of assets by ensuring they are running at peak efficiency. This leads to better product quality, higher production rates, and optimized resource utilization.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Through the use of IoT, AI, and machine learning, ARM provides real-time data on asset conditions, allowing businesses to make informed decisions about maintenance, replacement, and upgrades. This data-driven approach supports strategic planning and long-term growth.
By focusing on these core values, ARM enhances operational reliability, reduces risk, and positions companies for greater profitability and competitive advantage in their industries.
Interested in viewing the most recent webinar for a deeper comprehension?
Principles of Asset Reliability Management
The principles of Asset Reliability Management (ARM) are built on a proactive approach to maintaining and optimizing the performance of assets throughout their lifecycle. These principles focus on ensuring that assets are reliable, safe, and efficient by integrating strategies like predictive maintenance, condition monitoring, and data analytics.
By aligning maintenance practices with the actual condition of assets, ARM helps organizations minimize downtime, reduce costs, and extend asset lifespans. The core principles guide organizations in making informed decisions that enhance asset reliability, drive operational excellence, and ultimately contribute to business success.
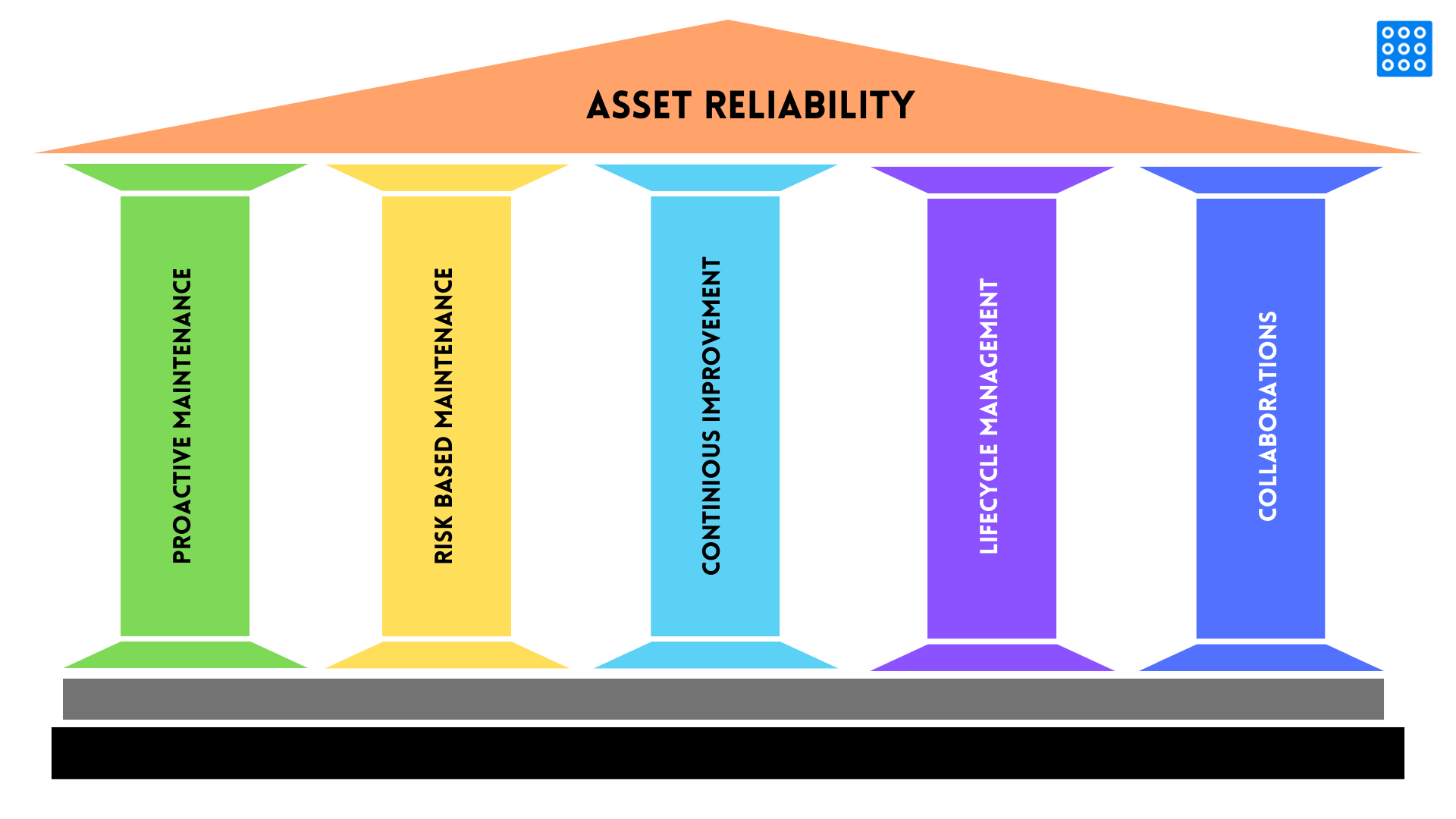
1. Proactive Maintenance Strategies:
Generally, Asset reliability is often achieved through proactive Maintenance. These approaches involve regularly inspecting, monitoring, and maintaining assets to identify and address potential issues before they result in equipment failures.
It is important to move from a reactive to a proactive maintenance approach for reliable plant operation. This transformation involves implementing preventive and predictive maintenance strategies to identify and address potential issues before they lead to equipment failure. Proactive Maintenance can significantly improve asset reliability and reduce unplanned downtime.
- Preventive Maintenance: Preventive Maintenance is scheduling maintenance tasks periodically to prevent equipment failures, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
- Predictive Maintenance: Using the data generated by assets, execute data analytics to forecast equipment issues, execute maintenance service, minimize downtime, and optimize performance predictably.
- Prescriptive Maintenance: Using the data generated by assets, identify and recommend specific maintenance tasks such as “replace filter” to optimize asset performance and prevent potential failures
2. Risk-based Maintenance:
Asset reliability management involves making decisions based on a thorough understanding of the risks associated with asset performance and reliability. The risk-based maintenance approach includes:
- Identifying and assessing potential failures.
- Understanding the consequences of those failures.
- Prioritizing actions based on risk mitigation.
Risk-based maintenance practice requires an IoT-based Asset Condition Monitoring solution to detect the health conditions of the asset to identify the potential risk factors.
In addition to detecting asset health conditions, performing root-cause analysis can identify underlying issues, address problems, and enhance overall reliability.
3. Continuous Improvement :
The continuous improvement practice establishes a culture by regularly reviewing asset management procedures. Continuous improvement ensures that asset reliability management strategies evolve and adapt to changing conditions, technologies, and business requirements.
- Maintenance Checklist:
Enforce maintenance checklists and capture operator feedback for continuous improvement based on past lessons learned from failures and successes.
- Maintenance Summary:
It is a health summary report prepared after maintenance tasks to provide a concise overview detailing activities, issues addressed, and equipment status for proactive decision-making.
4. Asset Life Cycle Management:
Asset lifecycle management involves tracking asset utilization and performance over time to understand downgrades that may lead to asset replacement. There are three key activities required to track the asset’s lifetime.
- Usage Metering:
Install an IoT-based automated metering system to read the usage level of the asset to keep track of up-to-date asset life. Tracks usage data for informed decision-making, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing efficiency.
- Maintenance History:
It required CMMS or Maintenance Software to keep track of all assets’ maintenance history, past activities, repairs, and inspections for insights into equipment performance and reliability.
- Warranty Management:
Keeping track of warranty information in a single repository helps to monitor warranty details for timely claims, cost savings, and effective risk management.
5. Collaboration:
Maintenance team collaboration is vital for efficient asset management. Shared expertise, effective communication, and coordinated efforts maximize productivity, enhance problem-solving, and ensure the longevity of critical equipment and systems.
Implement better collaboration among teams requires the following three key practices:
- Knowledge Management:
A knowledge management system must capture maintenance knowledge in a centralized system to organize and share insights for informed decision-making and continuous improvement.
- Team Communication:
Typically, different teams or shift engineers are involved in the maintenance operations, which require strong communication among themselves. Information sharing or messaging ensures seamless collaboration, quick issue resolution, and efficient task coordination for success.
- Data Accessibility:
Proving tools (e.g., mobile apps) to access maintenance data from anywhere facilitates easy retrieval for informed decisions, enhancing efficiency and optimizing asset reliability.
How to measure Asset Reliability?
To effectively measure the success and impact of Asset Reliability Management (ARM) practices, organizations rely on a variety of industry metrics that help track performance, identify areas for improvement, and ensure that reliability goals are being met.
These metrics provide valuable insights into the effectiveness of maintenance strategies, asset performance, and overall operational efficiency. Here are some key industry metrics that are commonly used to evaluate ARM practices:
1. Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF)
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) is one of the most widely used metrics in ARM. It measures the average time between asset failures during normal operation. A higher MTBF indicates better asset reliability and longer operational intervals between breakdowns.
This metric helps organizations evaluate how well their assets are performing and whether preventive maintenance strategies are effective in minimizing failure rates.
2. Mean Time to Repair (MTTR)
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) measures the average time it takes to repair an asset after a failure. This metric is crucial for assessing the efficiency of the maintenance team and the effectiveness of the organization’s response to unexpected breakdowns.
A lower MTTR indicates that the organization can quickly and efficiently restore assets to full functionality, minimizing downtime and operational disruptions.
3. Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is a comprehensive metric that evaluates the efficiency and performance of equipment, factoring in availability, performance, and quality. OEE provides insights into how well an asset or production line is performing relative to its full potential.
A higher OEE score indicates optimal asset utilization and reliability. OEE is particularly useful for identifying areas of improvement in asset performance and ensuring that downtime, speed losses, and defects are minimized.
4. Availability
Availability is a metric that measures the percentage of time an asset is ready for use and operational compared to the total time it is scheduled to be in service. It is a critical indicator of asset reliability, as higher availability means assets are operating at peak efficiency with minimal downtime.
This metric helps organizations determine how effectively they are maintaining their assets and how well they are managing unplanned downtime.
5. Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP)
Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) represents the proportion of maintenance activities that are scheduled in advance, as opposed to reactive or unplanned maintenance. A higher PMP indicates a more proactive approach to maintenance, which is a key component of ARM practices.
High levels of planned maintenance typically lead to fewer unplanned failures and disruptions, helping to reduce costs and improve asset reliability.
6. Asset Utilization Rate
Asset Utilization Rate measures the percentage of time an asset is actively used compared to the total available time. This metric reflects the efficiency with which assets are employed in production. High asset utilization rates indicate that equipment is being used effectively, contributing to higher overall productivity.
Low utilization may signal inefficiencies or underuse of critical assets, pointing to the need for better planning or reallocation of resources.
7. Cost of Maintenance as a Percentage of Asset Value
This metric measures the total cost of maintenance activities relative to the value of the assets being maintained. It helps organizations track the financial efficiency of their maintenance strategies.
A lower cost of maintenance as a percentage of asset value indicates that the organization is managing maintenance expenses effectively, while a higher percentage may suggest the need for improvements in reliability or the introduction of more cost-effective maintenance practices.
8. Failure Rate
Failure Rate measures the frequency at which assets or equipment fail within a specified period. This metric is crucial for assessing the reliability of individual assets or an entire asset fleet.
By tracking failure rates, organizations can identify problematic assets, recognize trends, and implement corrective actions to reduce failure occurrences. Lower failure rates are indicative of a successful ARM strategy that prioritizes reliability.
9. Maintenance Backlog
The Maintenance Backlog metric refers to the total number of maintenance tasks that are pending or overdue. A growing backlog can indicate inefficiencies in the maintenance process, lack of resources, or insufficient planning.
Keeping the maintenance backlog low is essential for maintaining asset reliability and ensuring that critical tasks are addressed promptly to avoid unexpected breakdowns.
10. Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) Effectiveness
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM) is a structured process for determining the most effective maintenance strategy for each asset. RCM Effectiveness measures the success of these strategies in reducing downtime, increasing reliability, and extending asset lifespan.
Organizations can track the effectiveness of their RCM practices by comparing pre- and post-implementation metrics like downtime reduction, cost savings, and asset performance improvements.
Benefits of Asset Reliability Management Across Industries
In today’s competitive manufacturing environment, asset reliability is a crucial factor for maintaining operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring high-quality production.
1. Automotive Manufacturing
In the automotive industry, where precision and efficiency are paramount, ARM ensures that machines and equipment are running at their best. Predictive maintenance can detect early signs of wear in production lines, preventing costly breakdowns and minimizing downtime.
This leads to improved production rates, higher-quality products, and fewer disruptions to supply chain schedules. ARM also contributes to enhanced safety by identifying potential hazards before they occur, reducing the risk of accidents on the production floor.
2. Food and Beverage Manufacturing
In the food and beverage sector, reliability management is essential to ensure compliance with health and safety regulations while maintaining consistent product quality. ARM helps prevent contamination, spoilage, and production delays caused by equipment failures.
With real-time monitoring and condition-based maintenance, manufacturers can schedule repairs during non-peak hours, avoiding disruptions to production. The result is increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved customer satisfaction with consistently high-quality products.
3. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
In the pharmaceutical industry, where precision and regulatory compliance are critical, ARM plays a significant role in maintaining equipment integrity. By ensuring that machines and systems are always operating at optimal levels, manufacturers can meet strict production standards and avoid contamination risks.
ARM helps companies avoid costly recalls and production delays, ensuring that pharmaceutical products are delivered on time and meet quality standards. Additionally, it supports compliance with industry regulations, providing traceability and documentation for maintenance activities.
4. Electronics Manufacturing
In electronics manufacturing, the pace of production is fast, and even small delays can disrupt the entire supply chain. ARM helps optimize the performance of sensitive equipment such as robotic arms, assembly lines, and testing machines.
By using predictive analytics to anticipate failures, manufacturers can avoid unexpected shutdowns and minimize repair costs.
ARM also contributes to energy efficiency by optimizing the performance of machinery, which is especially important in electronics manufacturing, where high energy consumption can drive up operational costs.
5. Aerospace Manufacturing
The aerospace industry relies heavily on the reliability and safety of equipment, as any malfunction can have serious consequences. ARM enables aerospace manufacturers to track the performance of critical assets, such as CNC machines and assembly robots, to detect potential issues before they affect production.
Predictive maintenance reduces the risk of unscheduled downtime, which can be costly in an industry where precision and deadlines are essential. By embracing ARM, aerospace manufacturers can improve product quality, reduce safety risks, and achieve higher operational efficiency.
6. Heavy Equipment and Machinery Manufacturing
In the heavy equipment and machinery sector, where large and complex assets are used, ARM ensures that equipment performs reliably under demanding conditions.
ARM helps manufacturers optimize the performance and lifespan of machines like cranes, excavators, and turbines, which are critical for operations in industries such as construction, mining, and energy.
By implementing predictive maintenance and condition-based monitoring, manufacturers can reduce repair costs, avoid catastrophic breakdowns, and extend the useful life of high-value equipment.
7. Textile Manufacturing
Textile manufacturers can benefit from ARM by reducing the impact of machine downtime on production lines. Equipment such as spinning machines, looms, and dyeing machines can experience wear and tear over time, leading to breakdowns that disrupt operations.
ARM helps identify potential issues early, allowing manufacturers to schedule maintenance during planned downtimes. This approach ensures smooth, continuous operations, higher product quality, and more efficient use of resources.
Fogwing CMMS for IoT Data-Driven Asset Reliability Management (ARM)
Fogwing CMMS Software is the comprehensive software for data-driven asset reliability operations. Fogwing CMMS offers the following features by default so that the maintenance team can practice the above five principles without pain.
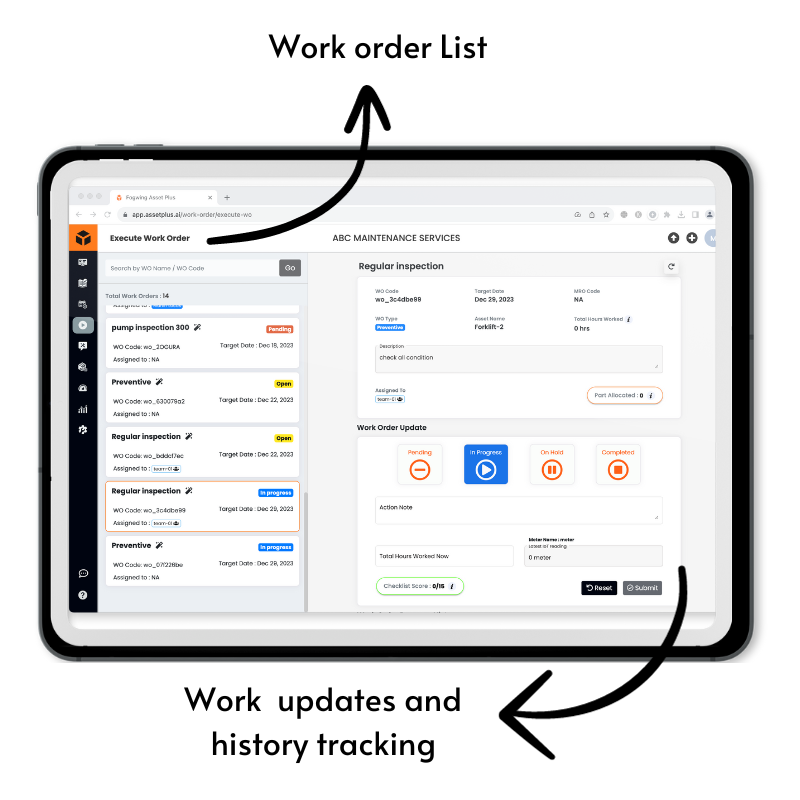
- Preventive Maintenance through automated scheduling.
- Condition-based Maintenance through IoT device connectivity
- Predictive maintenance recommendation based on sensor data
- AI-based maintenance checklist generation and enforcement
- Automated maintenance summary and user feedback capturing.
- In-built Asset Performance Monitoring
- Team communication through work order tasks summary
- Knowledge management through documentation repository for asset spec and instruction management.
- Maintenance history data accessibility through web and mobile application
Conclusion:
Implementing these principles in asset reliability management can help organizations enhance the performance, efficiency, and longevity of their assets while minimizing risks and improving overall operational reliability.

FAQs
1. What is Asset Reliability Management?
Asset Reliability Management (ARM) is the practice of ensuring physical assets—like machines, equipment, and tools—operate consistently without failure over time. It involves proactive maintenance, risk assessment, condition monitoring, and data-driven decisions to extend asset life, minimize downtime, and optimize performance.
2. What are the 5 principles of Asset Reliability Management?
The five core principles of Asset Reliability Management include:
- Proactive Maintenance Strategies – Preventive, predictive, and prescriptive approaches to avoid failures.
- Risk-Based Maintenance – Prioritizing tasks based on risk levels and asset health data.
- Continuous Improvement – Using insights and feedback to evolve maintenance practices.
- Asset Life Cycle Management – Tracking usage, history, and warranty to optimize asset life.
- Collaboration – Enabling team communication, data access, and knowledge sharing for effective reliability.
3. Why is Asset Reliability Management important in manufacturing?
ARM helps manufacturers reduce equipment downtime, control maintenance costs, improve product quality, and ensure operational safety. It keeps assets running efficiently, boosts production reliability, and strengthens a company’s competitive edge.
4. What is the difference between preventive and predictive maintenance?
Preventive maintenance is time-based—scheduled at regular intervals to prevent issues.
Predictive maintenance is condition-based—triggered by real-time data that signals early signs of failure.
Predictive maintenance is more efficient and reduces unnecessary work, especially when powered by IoT and AI systems.
5. How can IoT and AI be used for asset reliability management?
IoT devices collect real-time data on asset conditions, while AI analyzes this data to detect patterns and predict failures. Together, they enable smarter maintenance scheduling, automated alerts, and performance optimization. Fogwing CMMS combines both technologies for seamless asset reliability management.




