When something goes wrong, it’s natural to ask, “Why did this happen?” But finding the answer isn’t always straightforward. That’s where Root Cause Analysis (RCA) comes in—a process that helps uncover the real reason behind an issue so it doesn’t happen again.
What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a structured problem-solving methodology designed to identify the underlying causes of issues or failures rather than merely addressing their immediate symptoms.
By uncovering the root cause, organizations can implement effective and sustainable solutions to prevent the recurrence of similar issues. RCA is widely used across manufacturing, healthcare, IT, and utilities to improve quality, efficiency, and safety.
The ASQ (American Society for Quality) states that Root cause analysis can be traced to the broader field of total quality management (TQM). TQM has developed in different directions, including a number of problem analysis, problem solving, and root cause analysis..
Why is Root Cause Analysis Important?
RCA is critical for several reasons:
- Prevention of Recurrence: By identifying and addressing the root cause, organizations can prevent the same issue from happening again.
- Improved Quality: RCA leads to better quality control and assurance, ensuring consistent outputs.
- Cost Savings: Eliminating recurring issues reduces waste, rework, and downtime, thereby cutting operational costs.
- Enhanced Efficiency: RCA optimizes processes by resolving systemic issues that disrupt workflows.
- Risk Mitigation: It minimizes the risk of critical failures that could have severe consequences, such as safety hazards or financial losses.
Root Cause Analysis Methodologies
Several methodologies are commonly used to perform Root Cause Analysis, including:
- The 5 Whys: A simple iterative technique where the question “Why?” is asked multiple times until the root cause is identified.
- Fishbone Diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): A visual tool that categorizes potential causes under headings such as people, process, materials, equipment, and environment, making it easier to analyze contributing factors.
- Pareto Analysis: A statistical method that identifies the most significant issues contributing to a problem, based on the 80/20 rule.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): A systematic approach to identifying potential failure points, their causes, and effects to prioritize risks.
- Fault Tree Analysis (FTA): A top-down approach that starts with the problem and maps out all possible causes in a tree structure.
5 Why Analysis
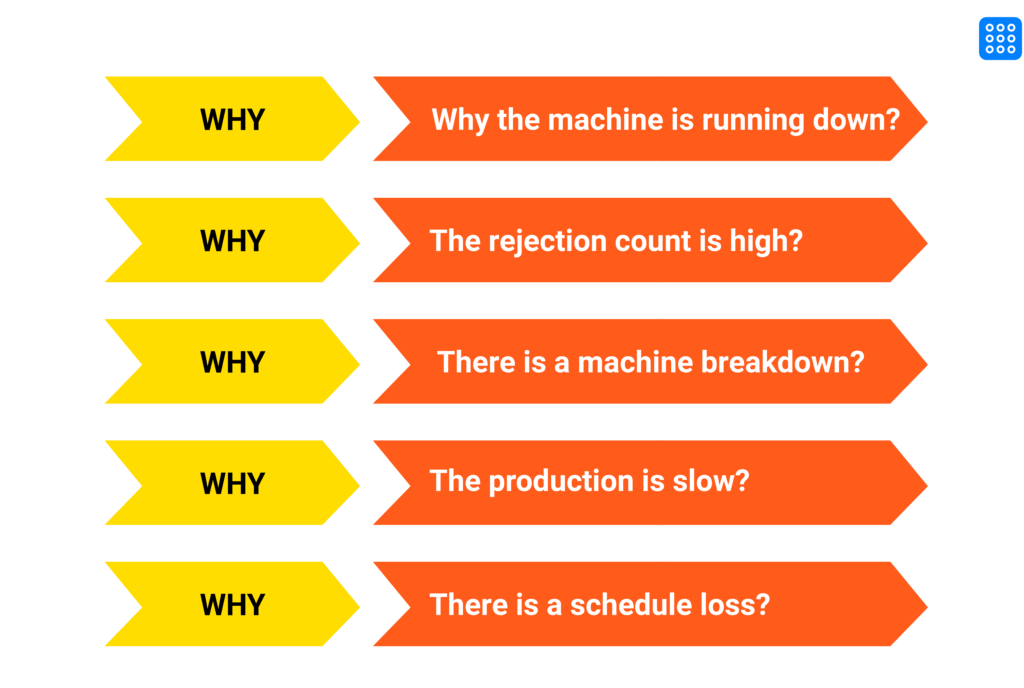
The 5 Whys is a straightforward iterative technique used to explore the root cause of a problem by repeatedly asking the question “Why?” until the foundational cause is identified. It typically takes five iterations to uncover the root cause, though this can vary based on the complexity of the issue.
- How It Works:
- Begin with the specific problem or issue.
- Ask “Why did this happen?” and record the answer.
- Use the answer as the basis for the next “Why?”
- Continue this process until the underlying cause is revealed.
Fishbone Analysis or Ishikawa Diagram

The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or Cause-and-Effect Diagram, is a visual tool used to systematically identify and analyze the potential causes of a problem. It helps categorize these causes into key areas to uncover the root cause effectively.
- How It Works:
- Draw a horizontal line representing the problem or effect on the right side of the diagram.
- Add branches (like a fish’s skeleton) for each major category of potential causes, such as People, Process, Materials, Equipment, Environment, and Methods.
- Under each category, list specific factors contributing to the problem.
Pareto Analysis
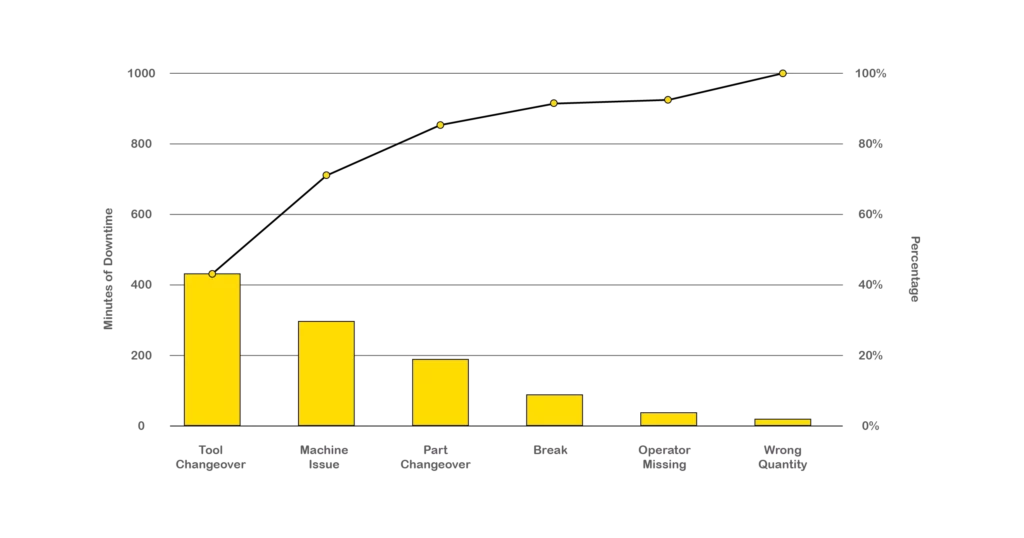
Pareto Analysis is a statistical technique based on the Pareto Principle (80/20 rule), which states that 80% of problems are often caused by 20% of the issues. This method helps identify and prioritize the most significant factors contributing to a problem, allowing organizations to focus their efforts effectively.
- How It Works:
- Collect data on the problem or issue.
- Categorize the causes and quantify their frequency or impact.
- Arrange the categories in descending order based on their significance.
- Plot the data on a Pareto Chart, with causes on the x-axis and their frequency or impact on the y-axis.
- Identify the critical few causes that account for the majority of the problem.
FEMA or Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a proactive approach to identifying potential failure points in a process, product, or system. It involves systematically evaluating possible failure modes, their causes, and their effects to prioritize risks and mitigate them effectively.
- How It Works:
- Identify the process or product to analyze.
- List potential failure modes (how something could fail).
- Determine the causes and effects of each failure mode.
- Assign risk priority numbers (RPN) based on the severity, occurrence likelihood, and detectability of each failure mode.
- Develop and implement actions to address high-priority risks.
Fault Tree Analysis or FTA
Fault Tree Analysis is a deductive, top-down methodology used to identify the possible causes of a specific undesired event or failure (known as the “top event”). It represents the causes in a tree-like diagram, showing the logical relationships between different contributing factors.
- How It Works:
- Define the undesired event (the top event) to analyze.
- Break down the causes of the top event into intermediate and basic events.
- Use logical gates (e.g., AND, OR) to represent the relationships between events.
- Continue until the basic events (root causes) are identified.
Who Should Perform RCA?
RCA is best conducted by a cross-functional team that brings diverse perspectives and expertise. This may include:
- Process Engineers: To provide technical insights into machinery and workflows.
- Quality Assurance Teams: To assess the impact on product or service quality.
- Operations Managers: To ensure alignment with organizational goals.
- Technicians and Operators: To offer hands-on knowledge of the equipment and processes involved.
- Safety Officers: To address any safety-related concerns.
Collaboration across departments ensures a holistic approach to identifying and addressing the root cause.
Read more detailed article about Root Cause analysis in Manufacturing.
When Should RCA Be Done?
RCA should be conducted in the following scenarios:
- After a Critical Incident: When a significant failure, safety breach, or system breakdown occurs.
- Recurring Problems: When the same issue repeatedly disrupts operations despite previous fixes.
- Deviations in Performance: When performance metrics fall below acceptable standards without an obvious explanation.
- Preventive Action Planning: As part of a proactive strategy to identify potential risks before they materialize.
- Customer Complaints: To address and resolve issues that impact customer satisfaction or product quality.
Role of Generative AI in Root Cause Analysis
Generative AI is revolutionizing Root Cause Analysis (RCA) by enhancing the speed, accuracy, and depth of problem-solving efforts. Leveraging advanced algorithms, machine learning models, and natural language processing, Generative AI automates various aspects of RCA while enabling more informed decision-making.
How Generative AI Enhances RCA?
- Data Analysis and Pattern Recognition: AI can analyze vast amounts of data from multiple sources, such as IoT devices, sensors, and historical records, to identify patterns and correlations that may indicate underlying causes of problems.
- Automated Diagnostics: By learning from past RCA efforts, AI can provide recommendations and insights to diagnose issues, even in complex systems.
- Scenario Simulation: Generative AI models can simulate various scenarios to predict potential causes of failures and their impacts, aiding in preventive measures.
- Real-Time Monitoring: AI-powered systems monitor processes continuously, alerting teams to anomalies and initiating RCA automatically when deviations occur.
- Knowledge Management: AI captures and organizes insights from previous RCAs, creating a knowledge base that assists in solving future problems more efficiently.
What is the benefits of using AI for Root Cause Analysis?
Leveraging Gen AI for RCA helps to enhance the outcome of the analysis faster and accurate.
- Speed: AI accelerates the RCA process by quickly sifting through large datasets.
- Accuracy: Reduces human error by relying on data-driven insights.
- Scalability: Handles complex systems with numerous variables more effectively than manual methods.
- Proactive Approach: Predicts issues before they arise, minimizing disruptions.
What challenges are in using AI for RCA?
- Requires high-quality data for accurate analysis.
- May need human oversight to validate AI-generated insights.
- Ethical considerations, such as data privacy and bias, must be addressed.
Conclusion
Root Cause Analysis is an invaluable tool for organizations striving to enhance quality, efficiency, and safety. By systematically identifying and addressing the underlying causes of problems, RCA helps prevent recurrence, reduce costs, and improve overall performance. Whether applied reactively or proactively, RCA enables organizations to achieve sustainable improvements and long-term success.




