In today’s competitive manufacturing landscape, achieving high levels of efficiency and maintaining top-notch quality are essential for success. The DMAIC process, derived from the Six Sigma approach, offers a structured methodology to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, reduce defects, and enhance overall performance. This blog will explore the DMAIC process, its benefits, and how its implementations optimize manufacturing operations.
What is DMAIC Process?
DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It is a problem-solving methodology widely used in six sigma projects to tackle process issues and variations. The DMAIC cycle provides a systematic framework that enables organizations to continually make data-driven decisions and enhance manufacturing processes.
DMAIC solves any number of problems in manufacturing, from simple issues like reducing scraps to more complex ones like streamlining production or improving quality control. When properly executed, it can significantly improve efficiency and quality.
DMAIC Methodology: A Six Sigma Approach
The DMAIC methodology approach is used in manufacturing to drive process improvement and achieve desired outcomes. It is a key component of the Six Sigma methodology. Organizations widely adopt it to reduce variation, defects, and waste.
Here is a breakdown of the five steps in the DMAIC methodology:
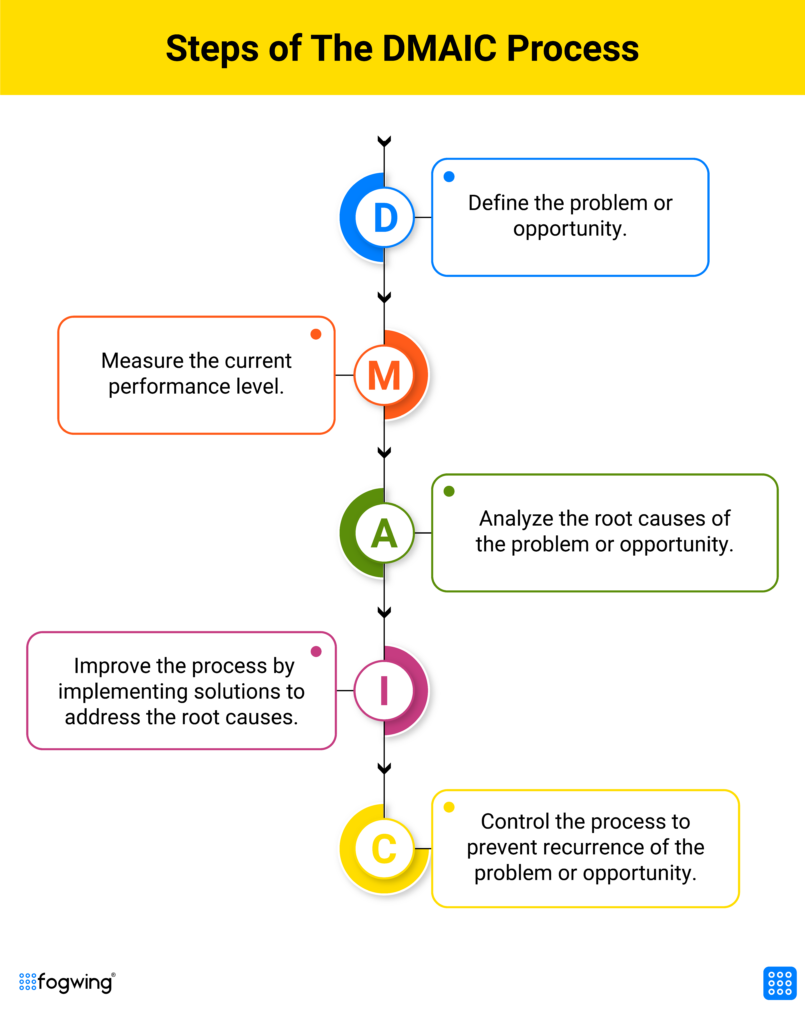
Define: This initial step of the DMAIC process clearly defines the project goals and objectives. The problem or area of improvement is identified, and the project’s scope is established. This step involves gathering input from stakeholders and setting specific targets for improvement.
Measure: Once the project is defined, the next step is to gather data to understand the current state of the process. Key metrics and performance indicators, such as cycle time, defect rate, and customer satisfaction, are identified and measured. This step helps establish a baseline and provides a quantitative understanding of the process.
Analyze: In the analysis phase of the DMAIC process, the collected data is studied to identify the root causes of problems or inefficiencies. Various tools like Pareto charts, fishbone diagrams, and statistical analysis methods identify the most significant sources of variation or defects. This step aims to gain insights into the underlying causes that must be addressed.
Improve: In the improvement phase; potential solutions are implemented and developed to address the root causes identified in the previous step. These solutions are tested on a small scale and refined before being implemented on a larger scale. The aim is to optimize the process and improve its performance based on the defined goals.
Control: The final step of the DMAIC process is focused on ensuring the improved process is sustained over time. Methods and systems are implemented to monitor the process performance and control any deviation from the desired outcome. Control plans are developed to ensure that the improvements are maintained and future issues are addressed promptly. By following the DMAIC six sigma methodology, manufacturing organizations can systematically identify and solve problems, enhance process efficiency, improve product quality, and achieve better overall performance.
DMAIC Tools and Techniques to Improve Quality & Efficiency
Several tools and techniques are employed during the DMAIC process, including:
- Process Mapping: Visual representation of the process flow to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Histograms: Graphical representation of data distribution to understand variations.
- Control Charts: Monitoring tools to assess process stability and identify deviations.
- Regression Analysis: Analyzing relationships between variables to determine their impact on outcomes.
- Lean Tools: Lean principles focus on eliminating waste and improving efficiency. DMAIC Tools like 5S (sort, set in order, shine, standardize, sustain), Value Stream Mapping, and Kaizen events optimize processes, reduce cycle time, and improve overall efficiency.
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): Identifying or diagnosing potential failure points and their consequences to mitigate risks.
Benefits of DMAIC in Manufacturing
DMAIC approach (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) offers numerous benefits to manufacturing companies. Let’s explore some of the key advantages:
Process Efficiency Improvement
DMAIC process helps identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks in manufacturing processes. By analyzing data and pinpointing root causes, organizations can streamline processes, reduce cycle times, and optimize resource utilization.
Quality Enhancement
DMAIC allows organizations to identify the sources of defects and variations in production. By addressing these issues, companies can significantly improve product quality, reduce rework, fewer customer complaints, and increase customer satisfaction.
Data-Driven Decision Making
The DMAIC process is data-centric, relying on real-time data rather than assumptions or guesswork. This data-driven approach ensures that decisions are taken based on evidence and are more likely to result in successful outcomes.
Cost Reduction
DMAIC helps reduce operational costs by eliminating waste and defects. Companies can save resources, minimize scrap, and lower the cost of rework, leading to improved financial performance.
Employee Engagement and Empowerment
DMAIC encourages cross-functional teamwork and collaboration. Involving employees in problem-solving and improvement initiatives fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering the workforce and increasing their engagement in the organization’s success.
Standardization and Consistency
DMAIC emphasizes establishing standard operating procedures (SOPs) to sustain improvements. Standardization ensures that processes are consistent, reducing variability and enhancing overall performance.
Risk Mitigation
The DMAIC process helps identify and mitigate potential risks in manufacturing processes through rigorous analysis and improvement measures. This proactive approach minimizes the likelihood of costly errors or product recalls.
Compliance and Regulations
DMAIC can help organizations meet and exceed compliance standards in industries with strict regulatory requirements. Companies can avoid penalties and legal complications by reducing defects and ensuring consistent quality.
Customer Retention and Loyalty
Improved product quality and reliability resulting from DMAIC implementation led to higher customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to remain loyal and recommend the company’s products to others, fostering brand loyalty.
Competitive Advantage
Companies that embrace DMAIC process and continuously improve their processes gain a competitive edge in the market. They can deliver products more efficiently, of higher quality, and with greater consistency, setting themselves apart from competitors.
Case Studies & Examples
Case Study 1: General Electric (GE)
Challenge: General Electric (GE), a multinational conglomerate, faced challenges in its manufacturing operations, resulting in increased defects, longer cycle times, and higher costs.
Solution:
Define: GE identified the problem areas, such as high defect rates and extended cycle times, and set specific goals for improvement.
Measure: Data on defects, cycle times, and other key performance metrics were collected to establish baselines and measure progress.
Analyze: The data analysis revealed the root causes of defects and inefficiencies, including equipment calibration issues and process variations.
Improve: GE implemented process improvements, including better equipment maintenance, operator training, and standard operating procedures.
Control: To sustain the improvements, GE established control measures and ongoing monitoring to prevent regressions.
Results: GE significantly reduced defects and cycle times, improving product quality and reducing costs.
The DMAIC approach enabled GE to streamline its manufacturing processes, enhancing efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Another well-known example of the DMAIC process at work is how it was used to improve the production of the Toyota Prius. Engineers used the DMAIC approach to identify and correct issues causing production delays in this case. As a result of their efforts, Toyota increased production of the Prius by 30%.

SFactrix, a DMAIC tool:
SFactrix production monitoring software supports the DMAIC methodology by providing the necessary data, analysis, and control features to drive continuous improvement efforts in the production process. SFactrix production monitoring solution helps define the problem or improvement opportunity by providing real-time data on production metrics. It allows users to identify specific issues and set clear goals for improvement.
SFactrix measures production data points such as cycle time, OEE, downtime, quality metrics, and overall productivity. It provides real-time measurements of the production process.
SFactrix production monitoring integrated with IoT offers advanced analysis of collected data to identify patterns, trends, and root causes of inefficiencies or quality issues. It also provides data visualization and reporting capabilities to facilitate real-time analysis and identify improvement opportunities that meet the DMAIC process goal.
SFactrix helps users generate ideas and prioritize improvement initiatives based on the analyzed data. It provides insights into areas where process interventions could lead to better performance, reduced downtime, improved quality, and increased productivity.
Once improvements are implemented, SFactrix helps control the changes by tracking the key performance indicators (KPIs), setting targets, and creating control charts. SFactrix also provides alerts and notifications if any deviations or downtime occur, allowing for timely corrective actions.
To read more about how to master the production monitoring goal with SFactrix, click here

Conclusion
The DMAIC process offers manufacturing companies a powerful tool to drive efficiency and enhance product quality. By following the Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control approach, organizations can identify the root causes of problems, develop practical solutions, and maintain continuous improvement. By embracing the DMAIC methodology and leveraging its tools, manufacturers can stay ahead in a highly competitive market, delight customers, and optimize their operations for long-term success.
FAQs
1.What is the DMAIC process in manufacturing, and why is it important?
The DMAIC process is a structured, data-driven methodology used in manufacturing to improve quality, reduce defects, and increase operational efficiency. DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, and it is a core part of the Six Sigma approach to continuous improvement.
Manufacturers use DMAIC to identify inefficiencies, understand root causes of process issues, and implement sustainable improvements—making it essential for enhancing product quality, reducing costs, and maintaining competitive advantage.
2.What are the five phases of the DMAIC methodology?
The DMAIC methodology includes five key phases:
- Define – Set clear project goals and identify problems.
- Measure – Collect and quantify data on current performance.
- Analyze – Investigate root causes using tools like Pareto charts and fishbone diagrams.
- Improve – Implement and test solutions to optimize performance.
- Control – Monitor results and standardize successful changes for long-term sustainability.
Each step in the DMAIC cycle is critical for ensuring quality assurance and process optimization in manufacturing.
3.What are some common DMAIC tools used to improve manufacturing processes?
Several tools support the DMAIC methodology, including:
- Process Mapping – Visualizing workflows to find inefficiencies.
- Control Charts – Monitoring process stability over time.
- Histograms and Pareto Charts – Analyzing data patterns and defect frequency.
- Regression Analysis – Exploring variable relationships.
- FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) – Identifying and mitigating potential risks.
- Lean Tools like 5S and Kaizen – Eliminating waste and boosting efficiency.
These tools empower manufacturers to make data-driven decisions and reduce process waste effectively.
4.What are the benefits of implementing DMAIC in manufacturing operations?
The DMAIC approach delivers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved process efficiency through waste and bottleneck reduction.
- Enhanced product quality by minimizing defects and rework.
- Cost savings via optimized resource use and lower operational expenses.
- Data-driven decision-making based on measurable KPIs.
- Employee engagement through cross-functional teamwork.
- Standardization and compliance with consistent SOPs and regulatory adherence.
- Customer satisfaction and retention due to better product reliability.
5.Can DMAIC help with regulatory compliance in manufacturing industries?
Yes, the DMAIC process supports regulatory compliance by promoting standardization and quality control. By reducing defects, documenting processes, and ensuring consistent outputs, manufacturers can meet or exceed industry standards and avoid penalties or recalls.




